About Docker
Docker is a program that performs os level virtualization, it can package an application and its dependencies in a virtual container that can run on any Linux server.
In this tutorial I will show you how to install Docker CE on Centos and basic concepts and commands. I am starting this by assuming you have the root privileges on your system if you are a non-root user with sudo privileges add a prefix ‘sudo’ on all commands I given below.
Install Docker
First update your system packages:
#yum update
Install the required dependencies:
#yum install yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2
Add docker stable repository to your system
#yum-config-manager –add-repo https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
Install the latest version of Docker CE using the command:
#yum install docker-ce
After the installation start the Docker daemon and enable it to automatically start at boot time:
#systemctl start docker
#systemctl enable docker
Output will be something like below image:
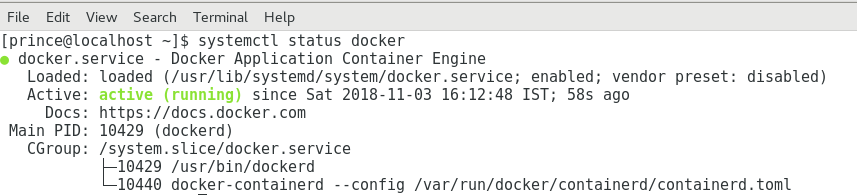
If you want to know Docker version:
#docker -v
Docker version 18.06.1-ce, build e68fc7a
Now we have a working Docker installation, the syntax of Docker commands is:
#docker [option] [subcommand] [arguments]
You can list all available docker command by just typing:
#docker

Docker Image Downloading
A Docker image is an immutable binary file including the application and all other dependencies such as binaries, libraries and instructions necessary for running the application. In short a Docker image is a snapshot of a Docker container.
The Docker Hub is a cloud-based registry service which is used for keeping the Docker images. One can put a docker image either in a public or private repository.
You can search docker images using the command:
#docker search [os_name]
For example, If you want to search all available ubuntu images in docker you can use the below command:
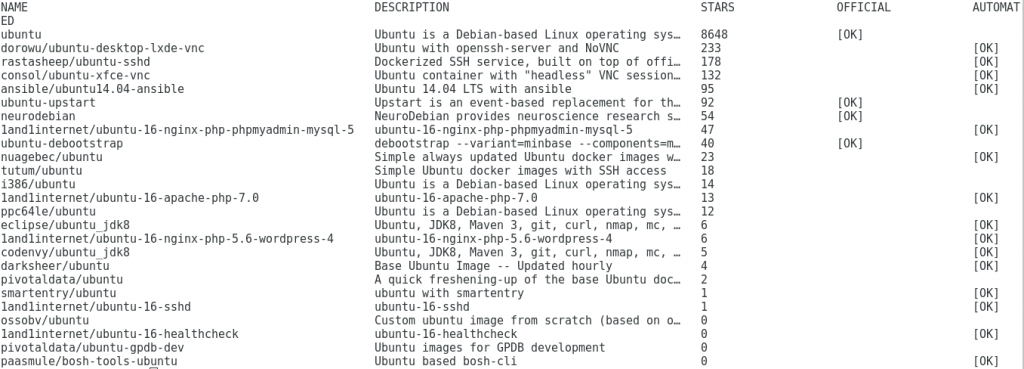
#docker search ubuntu
Output screen shows the list of available ubuntu images:
If you want to download ubuntu, you can do that by using the image pull command
#docker image pull ubuntu
Output:
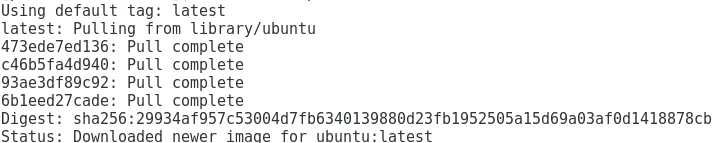
Depending on your Internet speed and the size of the image, download may take a few seconds or a few minutes.
Once the image is downloaded we can list the images with:
#docker image ls
Output screen seems like below:

If you want to delete an image you can do that with docker image rm [image_name] command:
For example:
#docker image rm ubuntu
The output shows:

Launching Docker Container
The docker run is the command used to launch Docker containers.
#docker run ubuntu
You can enter either image name or image ID here.
You can see the running containers using:
#docker ps
output:
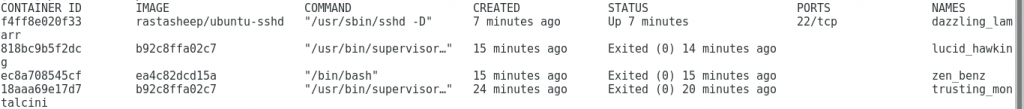
The switch -it allows us to interact with the container via the command line.
#docker run -it ubuntu /bin/bash